Anthropomorphising Technology: AI Avatars & Robots
What do these things have in common
Uncle Sam represents the United States of America. This figure is often depicted as a stern yet benevolent elderly man dressed in clothing that evokes the US flag, symbolizing patriotism and American values.
The Grim Reaper is an anthropomorphic representation of death. Typically depicted as a skeletal figure in a cloak wielding a scythe, the Grim Reaper personifies the concept of death in a human-like form, making the abstract idea more relatable and understandable
The Norse god Thor is depicted as a muscular man wielding a hammer, embodying human-like qualities of strength and heroism while representing thunder and storms
The animated film "Cars" features vehicles like Lightning McQueen and Tow Mater, which are cars that behave like people. They have faces, personalities, and engage in human-like interactions, making them relatable characters despite being inanimate objects.
Plants and Trees: In "Alice's Adventures in Wonderland," the daisies, pansies, and tulips engage in conversations and exhibit human-like behaviors and emotions.
Disney’s "The Lion King"
Pixar’s first movie "Toy Story,"
Anthropomorphism
Anthropomorphism is the attribution of human traits, emotions, or intentions to non-human entities. This can include animals, inanimate objects, or abstract concepts. The practice is often used in literature, art, and film to create relatable characters or to convey complex ideas through familiar human characteristics. This literary and artistic device enriches storytelling by making non-human elements more relatable and engaging to human audiences
Robots the ultimate form of Anthropomorphism
Robots represent the ultimate form of anthropomorphism because they are often designed to mimic human appearance, behavior, and cognitive functions, embodying the essence of attributing human-like qualities to non-human entities. This is evident in several ways:
Human-like Appearance:
Robots, especially humanoid robots, are designed with features that resemble humans, such as having a head, face, body, and limbs. This physical resemblance facilitates easier interaction with humans and makes robots more relatable. For instance, the presence of human features like eyelids can significantly increase the perception of humanness in robots, as mentioned in the study by DiSalvo et al. (2002)3.
Cognitive Functions:
Robots are often programmed to exhibit human-like cognitive abilities, such as learning, problem-solving, and decision-making. This not only makes them more effective in their tasks but also enhances their interactions with humans, making those interactions feel more natural and intuitive12.
Emotional Intelligence:
Some advanced robots are equipped with algorithms that allow them to read human emotions and respond appropriately, which can include expressing empathy or simulating emotional responses. This capability is crucial in roles that require social interaction, such as customer service or caregiving3.
Social Behaviors:
Robots can be programmed to understand and adhere to social norms and behaviors, engaging in conversations, recognizing social cues, and even exhibiting manners. These social capabilities are essential for robots intended for interactive roles in human environments
Robots are being trained in social behaviors using AI game simulations as a method to enhance their ability to interact effectively and naturally with humans. This training involves several key techniques and approaches:
Game-Based Learning Environments: As detailed in the source1, robots are increasingly deployed in game settings, which serve as controlled yet dynamic environments where robots can learn and practice social interactions. Games provide a structured setting with clear objectives and rules, making them ideal for teaching robots about human social norms and behaviors.
Simulating Human Behavior: In AI game simulations, robots are programmed to mimic human behaviors to better understand and replicate human social cues and interactions2. This involves using machine learning techniques to analyze and model human behavior patterns based on data collected from game play. By simulating these behaviors, robots can learn to predict and respond to human actions appropriately.
Social Interaction Scenarios: Within these game environments, robots are placed in various social interaction scenarios where they must navigate interactions with other artificial agents or human players1. This includes turn-taking, responding to social cues, and engaging in dialogues that are typical in human interactions. These scenarios help robots learn the subtleties of human communication and social etiquette.
Feedback and Reinforcement Learning: Robots use feedback from their performance in these games to improve their social behaviors. Techniques like reinforcement learning allow robots to learn from their actions by receiving rewards or penalties based on their decisions2. This method helps robots understand which behaviors are appropriate in different social contexts and adjust their actions accordingly.
Real-Time Interaction and Adaptation: Advanced AI algorithms enable robots to interact in real-time and adapt their behaviors based on the ongoing dynamics of the game1. This real-time processing is crucial for developing robots that can engage naturally with humans, as it allows them to respond immediately to changes in the environment or the behavior of human players.
Ethical and Social Considerations: Training robots in social behaviors also involves considering ethical and social implications, such as ensuring that the robots' behaviors are respectful and appropriate for all users. This includes programming robots to avoid biases and to treat all individuals with respect, regardless of background or characteristics1.
Transhumanism
Transhumanism is a philosophical and intellectual movement that aims to enhance the human condition through the development and widespread availability of advanced technologies that improve longevity, cognition, and well-being.
From a transhumanist perspective, human evolution with technology is not just a linear progression of tools and gadgets but a transformative journey towards enhancing and transcending our biological limitations. This journey encompasses the integration of digital, biological, and physical innovations to augment human capabilities, leading to a future where humans evolve into an enhanced species, or "posthumans." Here's an exploration of this evolutionary path, highlighting key milestones such as social media, digital twins, augmented reality, and the ultimate goal of transhumanism.
Social Media and the Digital Realm
The advent of social media marked a significant shift in human communication and interaction, leveraging digital technology to connect people across the globe instantly. Platforms like Facebook, Twitter, and Instagram have not only transformed social interactions but also influenced human behavior and cognition, potentially leading to permanent changes in our brains
.This digital revolution has expanded the scope of human experience, allowing us to share information, ideas, and personal messages, thereby creating online communities that transcend physical boundaries
AI-Powered Avatars and Digital Twins
The development of AI-powered avatars and digital twins represents a further step in human evolution with technology. These digital entities, which can mimic human speech, expressions, and mannerisms, offer a glimpse into the future of artificial intelligence and its potential to create lifelike virtual characters
Digital twins, in particular, serve as dynamic digital replicas of physical systems and processes, integrating real-time data, predictive analytics, and machine learning. This technology has the potential to transform various sectors, enhancing engagement and optimization processes by simulating the operation and performance of objects or systems
Augmented Reality and Enhanced Perception
Augmented reality (AR) technologies blend the digital and physical worlds, overlaying digital information onto the real world to enhance our perception and interaction with our environment. AR applications, ranging from gaming to education to healthcare, exemplify how technology can augment human sensory and cognitive capacities, offering enriched experiences that were previously unimaginable.
Transhumanism: The Integration of Bodies with Technology
Transhumanism represents the culmination of human evolution with technology, advocating for the use of science and technology to radically enhance human capabilities and improve the human condition. This philosophical and scientific movement envisions a future where humans transcend their biological limitations through the integration of technology, leading to the emergence of "posthumans" with augmented capabilities.
Transhumanists explore the potential of genetic engineering, cryonics, AI, nanotechnology, and other emerging technologies to achieve superintelligence, superlongevity, and superhappiness
Transhumanism also grapples with ethical, social, and philosophical questions about what it means to be human in an era of advanced technology. It challenges us to consider the implications of creating a society where diseases are eradicated, aging is reversed, and cognitive and physical abilities are significantly enhanced
The movement raises critical debates about access, equity, and the potential unintended consequences of such profound transformations
AI Avatars
AI avatars have become increasingly sophisticated, with advancements primarily driven by deep learning technologies. These avatars are designed to mimic human-like qualities, including facial expressions, behaviors, and interactions, making digital interactions more engaging and human-like
Avatars in Marketing
Functional Roles of Avatars
Functional roles of avatars in marketing are primarily task-oriented and involve direct interactions that assist customers or enhance operational efficiency. These roles include:
Virtual Assistants: Avatars can provide instant and automated customer support, answering frequently asked questions and resolving common issues efficiently, as mentioned in the EY article
Interactive Training and Onboarding: In a B2B context, avatars can be used for interactive training sessions, product demonstrations, and onboarding new employees, helping to streamline these processes
Data Analytics and Insights: Avatars can assist in gathering and analyzing data from customer interactions, enabling businesses to tailor their marketing and sales strategies more effectively
Supply Chain and Logistics: Avatars can be integrated into supply chain management, offering personalized guidance and support in logistics operations
Security and Authentication: Avatars can also play a role in enhancing security measures, such as through biometric authentication or as part of compliance processes
SK-II:
The Japanese skincare brand created YUMI, an AI-powered brand avatar ambassador, to answer customer questions and provide personalized beauty advice. YUMI represents a functional role in customer support, offering instant and automated assistance to customers seeking information about SK-II products.
Maruti Suzuki:
Integrated AI Avatars on their digital channel as part of a pilot with DaveAI. The virtual sales avatar 'Dave' appeared on the Maruti Suzuki website and replicated an actual salesperson for customers. Customers could ask various queries about car features, demonstrating the avatar's role in interactive product demonstrations and enhancing the customer buying experience
Samsung:
Uses a digital human avatar named Sam to provide customer service on its website. Sam can answer customer questions about Samsung products and services and can even help customers place orders. This example showcases the use of avatars as virtual assistants that offer instant and automated customer support
Bank of America:
Uses a digital human avatar named Erica to provide customer service on its mobile app. Erica can answer customer questions about their bank accounts and help customers with transactions such as transferring money and paying bills. Erica's role exemplifies how avatars can be used for security and authentication, ensuring secure transactions and customer interactions
Since launching in 2018, Erica® has helped nearly 32 million Bank of America clients manage their financial lives
Erica, the most advanced and first widely available virtual financial assistant, has surpassed 1 billion interactions with Bank of America clients. The award-winning technology, powered by artificial intelligence (AI), officially launched in 2018 and has since helped nearly 32 million clients with their everyday financial needs.
“Erica is the definition of how Bank of America is delivering personalization and individualization at scale to our clients,” said David Tyrie, Chief Digital Officer and Head of Global Marketing at Bank of America. “We expect the second billion to come even more quickly as we continue to evolve Erica’s capabilities, providing clients with the shortest route to the answers they need about their financial lives.”
Since its launch, Erica has expanded to include new features and functionality:
Clients viewed 37 million proactive insights to help them review their finances and cut recurring subscription charges that may have increased unexpectedly, know when they’ve received a merchant refund, or have duplicate charges.
More than 4 million proactive notifications about eligibility for Preferred Rewards have helped clients enroll in the program and enjoy the benefits.
60 million Spend Path insights have helped clients understand their finances with a weekly snapshot of spending.
More than 98% of clients get the answers they need using Erica. In September 2022, the bank launched Mobile Servicing Chat by Erica to connect clients for a live chat with representatives to answer more complex servicing questions, with more than 170,000 chats having already taken place
Coming in the first half of 2023, Erica will connect clients to financial specialists when they have questions about new products and services, such as a mortgage, credit card or deposit account.
“Bank of America has invested $3 billion or more on new technology initiatives each year for over a decade, including significant investments in AI that allow us to deliver a seamless user experience and industry-leading personalization for our clients banking online or on their mobile devices,” explains Aditya Bhasin, Chief Technology & Information Officer. “Our continued investment in Erica’s AI-powered capabilities enables us to quickly respond to voice, text chat or on-screen interactions from clients who need assistance with financial transactions, and to proactively deliver personalized insights and advice at key moments.
As Erica’s capabilities have grown, so has its ability to help clients across their entire banking, lending and investing relationship with Bank of America, including Merrill Edge, Bank of America Private Bank and Benefits Online. Erica also supports Merrill clients through insights on portfolio performance, trading, investment balances, quotes and holdings and can help connect clients to a Merrill advisor. Additionally, bankers who support business clients at Bank of America use BankerAssist, an AI virtual assistant leveraging the underlying technology of Erica, to identify and close new opportunities, manage exposure and use real-time data to further client conversations.
Yoox:
This Italian e-commerce platform launched Yoox Mirror, a virtual fitting room where shoppers could interact with a digital avatar called Daisy. This avatar could be fully customized to resemble the buyer, allowing them to edit and view different looks. This represents the use of avatars in interactive training and onboarding, as well as in customization and personalization, by providing a unique shopping experience that helps customers make informed purchasing decisions
These examples highlight how brands are leveraging avatars in functional roles to improve customer engagement, streamline operations, and enhance the overall marketing strategy. Avatars serve as virtual assistants, interactive product demonstrators, and personalized customer support agents, showcasing the potential of digital avatars in transforming business operations and customer interactions
Non-Functional Roles of Avatars
Non-functional roles of avatars are more related to branding, storytelling, and creating an immersive experience for customers. These roles include:
Brand Ambassadors: Avatars can personify brand characteristics, enhancing consumer perceptions and fostering a stronger brand connection. They can represent the brand at virtual events, participate in discussions, and interact with attendees
Storytelling and Engagement: Avatars can facilitate brand storytelling and create memorable brand experiences. They can be incorporated into marketing campaigns, animated videos, or advertisements, boosting brand awareness and customer loyalty
Social Media Interaction: Brands can create social media accounts for avatars to interact with their audience, share content, and promote the brand in a unique and recognizable way. AI-generated social media influencers are redefining marketing strategies by offering a unique blend of reliability, customization, and cost-efficiency. These digital entities can generate content autonomously, engage with real-time trends, and mimic human emotions, making them valuable assets in social media marketing.
Extension of Brand Identity: Avatars can become iconic symbols of the brand in the digital space, akin to traditional mascots or spokespersons, and can evolve with the brand over time
Consumer Touchpoints: Avatars can revolutionize consumer interactions by serving as interactive touchpoints, providing personalized recommendations, and adapting their personalities based on user preferences
Here are some examples of brands using avatars for non-functional roles in marketing, which focus on enhancing brand identity, storytelling, and creating immersive customer experiences:
Louis Vuitton:
The luxury fashion brand introduced a virtual boy named "Vivienne" as a digital ambassador who travels through various gaming worlds, collecting items and showcasing the brand's products. This avatar not only serves as a brand ambassador but also engages customers through storytelling and interactive experiences, enhancing the brand's appeal to younger, digitally-savvy audiences.
Gucci:
Collaborated with Genies to allow users to create their own digital avatars wearing Gucci clothing. These avatars can be used on social media platforms, enhancing user engagement and allowing Gucci to tap into the virtual goods market. This initiative serves as an extension of Gucci’s brand identity into the digital realm, making it more accessible and relatable to a tech-oriented demographic.
Balmain:
Partnered with the virtual band Shudu, Margot, and Zhi, who are digital supermodels created using CGI technology. These avatars appeared in Balmain's advertising campaigns and social media, helping to tell the brand's story in a unique and modern way. This approach not only enhances storytelling but also solidifies Balmain's position as an innovative leader in digital fashion.
Warner Music Group:
Created a virtual influencer named Tia, who has her own social media presence and engages with fans just like a human influencer would. Tia shares content related to music and lifestyle, participates in discussions, and interacts with followers, thereby boosting brand awareness and engagement for Warner Music Group.
IKEA:
Used a virtual influencer named Imma in their marketing campaigns. Imma, known for her distinctive pink hair, was featured in various IKEA store setups, appearing to live in and interact with IKEA-designed rooms. This campaign used storytelling and engagement to create a memorable brand experience that resonated with younger audiences.
Nissan:
Introduced a virtual host named "Nissan Sakura" for their online showroom. Sakura interacts with online visitors, providing information about Nissan's electric vehicles and answering customer queries. This avatar enhances the customer experience by serving as an interactive touchpoint that offers personalized assistance, making the virtual showroom more engaging and informative.
Technology
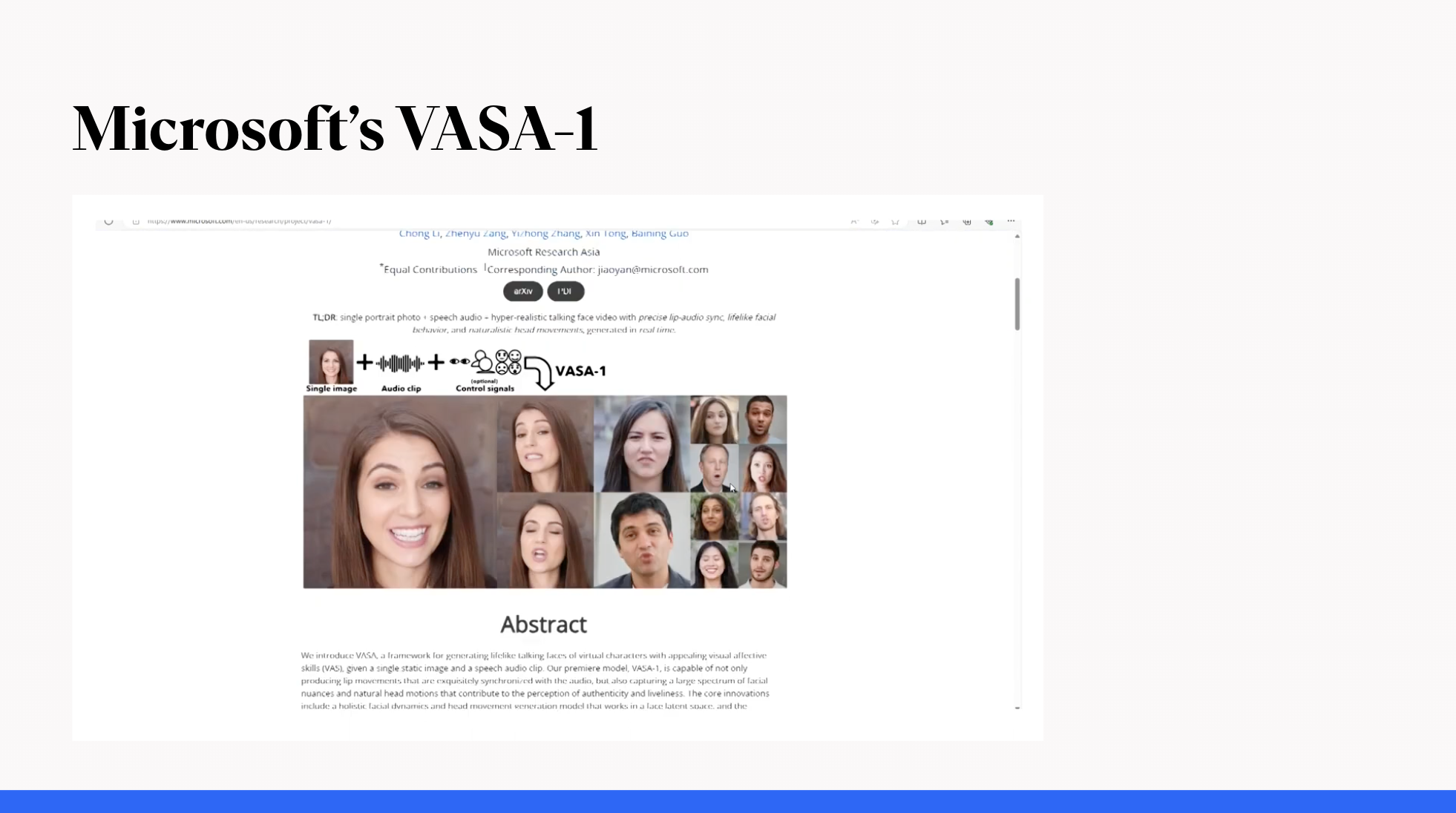
Microsoft's VASA-1 model
Recent innovations include the development of more realistic avatars facilitated by the availability of extensive data capturing detailed human expressions and movements. For example, Microsoft's VASA-1 model can create animated videos of a person talking with synchronized lip movements from just a single image and a speech audio clip
Microsoft's VASA-1 model is an advanced AI system designed to generate lifelike talking faces from a single static image and an audio speech track. Here are the key details about the VASA-1 model based on the provided sources:
Overview and Capabilities
VASA-1 stands for Visual Affective Skills Animator, with "VAS" indicating its focus on visual affective skills.
The model can produce realistic talking faces with accurate lip-syncing, natural facial expressions, and head movements that are synchronized with the audio input
It goes beyond simple mouth movement mimicry, capturing a wide range of human-like emotions and producing natural-looking movements2.
The system allows for manipulation of various parameters such as pitch, speed, face orientation, and emotions1.
VASA-1 can generate specific facial expressions, synchronize lip movements, and produce human-like head motions
The technology is capable of handling types of photos and audio inputs that were not in the training dataset, such as singing audio, artistic photos, and non-English speech
Technical Aspects
The model's realism stems from a 'disentanglement' process, which enables independent control of facial expressions, 3D head position, and facial features2.
It can generate high-resolution videos (512×512 pixels) at 45 frames per second (fps) in offline mode and 40 fps with online generation2.
VASA-1 was trained on the VoxCeleb2 dataset, which contains over 1 million utterances for 6,112 celebrities, extracted from YouTube videos3.
Potential Applications
The technology has potential use cases in gaming, social media, filmmaking, customer support, education, and therapy
It could enhance educational equity, improve accessibility for individuals with communication challenges, offer companionship or therapeutic support, and more
Ethical Considerations and Release Status
Microsoft has refrained from making VASA-1 publicly available due to concerns over its potential misuse for producing deceptive content or impersonating individuals1
The company emphasizes the importance of responsible use and proper regulations before considering a public release
Microsoft is exploring VAS generation only for virtual interactive characters and not for impersonating any real-world person
Comparison with Other Models
VASA-1 is compared favorably to similar technologies from companies like Runway, Nvidia, Google, and Alibaba, with experts noting its higher quality and realism
It is capable of making the face move in three dimensions and the eye gaze move in different directions, which makes it much more realistic than some other models
Concerns and Future Directions
Observers have flagged that VASA-1 makes it easier to create deepfakes, and there is potential for misuse
Microsoft is also exploring ways to apply their technique for advancing forgery detection
The model is currently a research demonstration, and Microsoft has no plans to release an online demo, API, product, additional implementation details, or any related offerings until it is certain that the technology will be used responsibly6.
In summary, Microsoft's VASA-1 model represents a significant advancement in AI-driven video generation, offering the ability to create realistic talking avatars from a single image and audio track. While the technology holds immense potential for various applications, ethical considerations and the potential for misuse have led Microsoft to proceed cautiously with its release
Eleven Labs
Eleven Labs' voice cloning technology operates through a sophisticated process that involves several technical steps to create a realistic and natural-sounding AI voice model. Here’s a detailed explanation of how the technology works:
Step-by-Step Process of Voice Cloning at Eleven Labs
Voice Recording and Collection: The first step in the voice cloning process involves recording or collecting high-quality audio samples of the voice to be cloned. It is crucial that these recordings are clear and free from background noise to ensure the accuracy of the voice model.
Feature Extraction: Once the audio samples are collected, the next step is to analyze the voice and extract distinctive features. This analysis breaks down the audio into phonemes, which are the smallest units of sound in a language. The system also identifies unique aspects of the voice such as accent, intonation, and rhythm. These features help in distinguishing the specific characteristics of the voice.
Training the AI Model: The extracted features are then used to train an AI model, typically a type of neural network. This training process involves feeding the AI system with the voice data, allowing it to learn and replicate the specific characteristics of the voice. The model adjusts its parameters to minimize the difference between the output it generates and the original voice samples
Synthesis and Fine-Tuning: After the model has been trained, it can generate new speech that mimics the original voice. This generated speech is then fine-tuned to ensure it sounds natural and matches the nuances of the original voice. The fine-tuning process may involve adjusting various elements like tone, pitch, and speed to perfect the cloned voice.
Output Generation: The final step is the generation of the cloned voice output. The AI model uses the trained data to synthesize speech that can say anything within the bounds of the programmed language, maintaining the style and tone of the original voice. This output can then be used in various applications such as virtual assistants, audiobooks, or any other medium that requires voice synthesis.
Technical Considerations
Quality of Voice Output: The realism and naturalness of the cloned voice are critical. Eleven Labs focuses on capturing the subtle nuances and inflections of the original voice, which are essential for creating a convincing clone3.
Multilingual Support: Eleven Labs supports cloning voices in multiple languages, which is beneficial for creating diverse voice models that can cater to a global audience.
Privacy and Security: Ensuring the privacy and security of the voice data is paramount. Eleven Labs implements robust security measures to protect the data used in voice cloning processes.
In summary, Eleven Labs' voice cloning technology involves a detailed process of recording, analyzing, and training an AI model with voice data to create a realistic and natural-sounding voice clone. This technology leverages advanced machine learning techniques and neural networks to replicate human voice characteristics accurately, offering significant opportunities in various fields where voice interaction is essential.
Avatars & LLMs
Connecting avatars with Large Language Models (LLMs) for conversational AI involves integrating advanced natural language processing (NLP) capabilities with digital representations of humans or characters to create interactive, conversational agents. This integration allows avatars to understand and generate human-like text, enabling them to engage in natural and coherent conversations with users. The process typically involves several key components and technologies, including LLMs, speech recognition and synthesis, and avatar animation technologies.
Large Language Models (LLMs)
LLMs, such as those discussed in the sources, are at the core of conversational AI avatars
These models are trained on vast amounts of text data, enabling them to understand language, generate responses, and even exhibit certain personality traits or conversational styles
By leveraging LLMs, avatars can provide more engaging and human-like interactions, ranging from customer service applications to educational tools and entertainment
Integration and Deployment
Integrating LLMs with avatars involves connecting the language understanding and generation capabilities of the LLM with the avatar's speech and animation systems
This can be achieved through APIs and software development kits (SDKs) that allow developers to embed these capabilities into various platforms and applications
The integration enables avatars to not only understand and respond to user queries in real-time but also to exhibit lifelike animations and expressions that enhance the overall user experience
RAG & Product Recommendations
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) is a powerful technique that enhances the capabilities of product recommendation systems by integrating external knowledge sources to provide more accurate, relevant, and personalized recommendations. This approach leverages the strengths of both generative AI models and information retrieval systems to address the limitations of traditional recommendation engines.
How RAG Works in Product Recommendations
Integration of External Knowledge
RAG systems enhance product recommendation engines by accessing a vast array of external data sources, such as product databases, customer reviews, and even real-time user interaction data. This allows the system to retrieve information that is not only relevant to the user's current query but also enriched with context that improves the recommendation's relevance and personalization
Dynamic Response Generation
Once relevant information is retrieved, RAG utilizes generative AI models to synthesize this data into recommendations that are tailored to the user's preferences and needs. This process involves analyzing the retrieved data to understand deeper nuances such as user sentiment, product popularity, and emerging trends, which traditional recommendation systems might overlook
Continuous Learning and Adaptation
RAG systems are designed to continuously learn from new data, allowing them to adapt to changes in user behavior and preferences over time. This dynamic learning capability ensures that the recommendations remain relevant and effective, even as market conditions and consumer trends evolve
Benefits of RAG in Product Recommendations
Enhanced Personalization
By leveraging a broader range of data sources, RAG enables recommendation systems to offer highly personalized suggestions that are more likely to meet individual user preferences and requirements. This personalization is achieved by understanding the context of user interactions and integrating insights from external data sources
Improved Accuracy and Relevance
RAG helps in reducing the common problem of irrelevant recommendations in traditional systems. By using up-to-date external information, RAG ensures that the recommendations are accurate and based on the most current data, thereby increasing the likelihood of user engagement and satisfaction
Reduction in Bias and Hallucination
Traditional recommendation systems often suffer from bias and hallucinations, where the system might generate misleading or incorrect suggestions based on incomplete or biased training data. RAG addresses this issue by grounding the recommendations in real-world data, thus providing more objective and balanced suggestions
Scalability and Flexibility
RAG architectures are inherently scalable and can handle large-scale data from diverse sources. This scalability makes RAG suitable for large e-commerce platforms where the volume of products and user interactions is enormous. Additionally, the flexibility of RAG allows it to be adapted for various types of products and user demographics
Use Cases in Real-World Applications
Several companies have successfully implemented RAG in their product recommendation systems. For instance, e-commerce platforms use RAG to enhance their recommendation engines by integrating user reviews and real-time interaction data to provide personalized product suggestions. Similarly, media streaming services apply RAG to recommend movies or music based on a user's viewing history and preferences extracted from external databases
In summary, Retrieval-Augmented Generation significantly enhances product recommendation systems by providing a more personalized, accurate, and user-centric shopping experience. By effectively integrating generative AI with external data retrieval, RAG enables recommendation engines to adapt to user needs dynamically and offer suggestions that are timely, relevant, and highly personalized
Benefits of Enhanced Memory
The enhanced memory capabilities provided by RAG lead to several benefits in conversational AI applications:
Improved User Satisfaction: By maintaining context over multiple interactions, users feel understood and valued, leading to higher satisfaction and engagement.
Efficiency in Handling Queries: RAG's ability to remember and retrieve relevant past interactions reduces the need for users to repeat information, streamlining the conversation process.
Personalization: Access to historical interactions enables the system to tailor its responses more effectively to individual user preferences and history
Size of the Market
The AI avatar market is projected to reach various values by 2032 according to different sources:
According to Spherical Insights & Consulting, the global digital avatar market size is expected to reach USD 283.47 billion by 2032
Market.us estimates the digital avatar market will achieve a value of USD 533.8 billion by 2032
Polaris Market Research predicts the market will reach USD 506.46 billion by 2032
.These projections indicate significant growth in the market, driven by advancements in technology and increasing applications across various industries.
Social Media Influencers vs. AI Influencers
Examples and Economic Aspects
Notable AI influencers include Lil Miquela and Aitana Lopez, who have garnered significant followings and engage in marketing campaigns
These influencers represent a shift towards virtual models that can operate without the limitations of human influencers, such as availability or ethical concerns
To compare the earnings of social media influencers with AI avatars and predict when AI avatars might outearn social media influencers, we need to analyze the available data on their respective earnings and market growth.
Social Media Influencers' Earnings
Macro-influencers: Influencers with over 1 million followers earn about $1,804 per post11.
Average Earnings: Across various platforms, social media stars receive different payments per post. For example, Instagram influencers earn between $1,315 to $2,643 depending on their follower count and gender15.
Overall Market Size: The influencer marketing industry is valued at $21.1 billion16.
AI Avatars' Market Value and Predicted Growth
Current Market Size: The global digital avatar market size was valued at USD 7.55 billion in 2022 and is projected to grow to USD 283.47 billion by 20326.
Growth Rate: The market is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 43.7% from 2022 to 20326.
Analysis and Prediction
Current Earnings: Social media influencers, particularly those with large followings, can earn substantial amounts per post, with top influencers earning thousands of dollars for a single piece of content. However, these earnings are highly variable and depend on factors such as follower count, engagement rate, and the platform used.
AI Avatars' Market Growth: The AI avatar market, although starting from a lower base, is projected to experience a rapid growth rate. This growth is driven by advancements in technology and increasing applications across various industries.
Predicting Crossover: Given the rapid growth rate of the AI avatar market (43.7% CAGR), it is projected to reach a market size of USD 283.47 billion by 2032. In contrast, the influencer marketing industry, while substantial, has a lower overall market valuation and growth rate.
The regulations around AI avatars encompass a variety of legal and ethical considerations, primarily focusing on intellectual property rights, privacy, data protection, and the potential for misuse. Here’s a summary based on the provided sources:
Intellectual Property Rights
Copyright Issues: AI-generated images, including avatars, often involve complex copyright issues, particularly concerning the data used to train AI models. There is a risk of copyright infringement if the AI copies or is trained on copyrighted material without proper authorization.
Ownership and Control: The creation and use of AI avatars involve considerations about who owns the rights to the avatars and how they can be used, especially when they are based on real people's likenesses.
Privacy and Data Protection
Personal Data Use: AI avatars often require personal data to create personalized or realistic representations. This raises concerns about privacy and the secure handling of such data, especially under regulations like the GDPR in the European Union, which mandates strict data protection and privacy standards.
Biometric Information: Specific laws like the Illinois Biometric Information Privacy Act (BIPA) regulate the use of biometric data, which can include facial recognition technologies used in creating AI avatars. These laws typically require informed consent for collecting and using biometric data.
Ethical and Misuse Concerns
Misrepresentation and Deception: There is a potential for AI avatars to be used in misleading or deceptive ways, such as impersonating real individuals without consent. This can lead to ethical and legal issues around misrepresentation and fraud.
Discrimination and Bias: AI systems, including those used to create avatars, can perpetuate biases present in the training data, leading to discriminatory outcomes. This is a concern under anti-discrimination laws and ethical guidelines.
Regulatory Frameworks and Guidelines
Emerging Regulations: While specific laws directly regulating AI avatars are still developing, existing laws on copyright, privacy, and data protection are applicable. Discussions around new regulations, such as the EU’s AI Act, are ongoing and may set precedents for more specific rules concerning AI avatars.
Ethical Guidelines: Various ethical guidelines recommend principles such as transparency, accountability, and respect for user privacy and rights when developing and using AI technologies, including avatars.
Practical Implementation
Terms of Service and User Agreements: Companies creating AI avatars often outline the rights, responsibilities, and restrictions associated with their use in terms of service or user agreements. These documents are crucial for ensuring users understand and agree to how their data and likenesses are used.